Who Screens The Sunscreens?
Yesterday, we asked about your sunscreen policy and received mixed responses. One subscriber shared their personal experience with melanoma, emphasizing the importance of sun protection for their active family.
We Screen The Sunscreens!
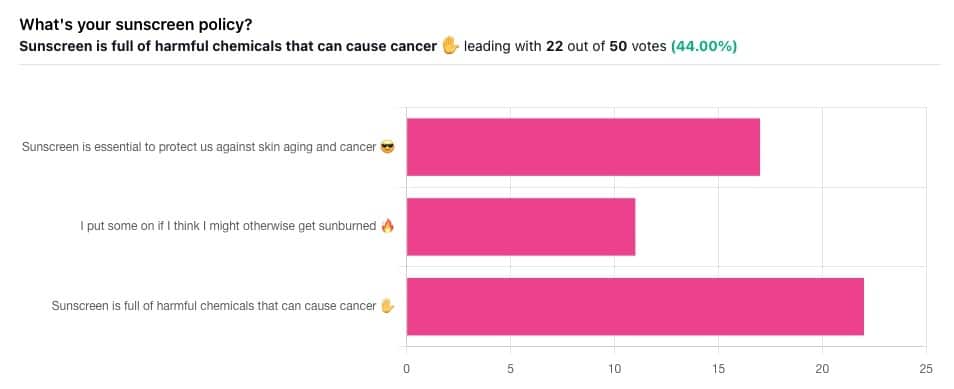
Yesterday, we asked you what your sunscreen policy was, and got a spread of answers. Apparently this one was quite polarizing!
One subscriber who voted for “Sunscreen is essential to protect us against skin aging and cancer” wrote:
❝My mom died of complications from melanoma, so we are vigilant about sun and sunscreen. We are a family of campers and hikers and gardeners—outdoors in all seasons—and we never burn❞
Our condolences with regard to your mom! Life is so precious, and when something like that happens, it tends to stick with us. We’re glad you and your family are taking care of yourselves.
Of the subscribers who voted for “I put some on if I think I might otherwise get sunburned”, about half wrote to express uncertainties:
- uncertainty about how safe it is, and
- uncertainty about how helpful it is
…so we’re going to tackle those questions in a moment. But what of those who voted for “Sunscreen is full of harmful chemicals that can cause cancer”?
Of those, only one wrote a message, which was to say one has to be very careful of what is in the formula.
Let’s take a look, then…
Sunscreen is full of harmful chemicals that can cause cancer: True or False?
False—according to current best science. Research is ongoing!
There are four main chemicals (found in most sunscreens) that people tend to worry about:
- Abobenzone
- Oxybenzone
- Octocrylene
- Ecamsule
Now, these two sound like four brands of rocket fuel, but then, dihydrogen monoxide (DHMO), which is also found in most sunscreens, sounds like a deadly toxin too. That’s water, by the way.
But what of these four chemicals? Well, as we say, research is ongoing, but we found a study that measured all four, to see how much got into the blood, and what adverse effects, if any, this caused.
We’ll skip to their conclusion:
❝In this preliminary study involving healthy volunteers, application of 4 commercially available sunscreens under maximal use conditions resulted in plasma concentrations that exceeded the threshold established by the FDA for potentially waiving some nonclinical toxicology studies for sunscreens. The systemic absorption of sunscreen ingredients supports the need for further studies to determine the clinical significance of these findings. These results do not indicate that individuals should refrain from the use of sunscreen.❞
Now, “exceeded the threshold established by the FDA for potentially waiving some nonclinical toxicology studies for sunscreens” sounds alarming, so why did they close with the words “These results do not indicate that individuals should refrain from the use of sunscreen”?
Let’s skip back up to a line from the results:
❝The most common adverse event was rash, which developed in 1 participant with each sunscreen.❞
This was most probably due to the oxybenzone, which can cause allergic skin reactions in some people.
Let us take a moment to remember the most common adverse event that occurs from not wearing sunscreen: sunburn!
You can read the full study here:
None of those ingredients have been found to be carcinogenic, even at the maximal blood plasma concentrations studied, from applications 4x/day to 75% of the body.
UVA rays, on the other hand, are absolutely very much known to cause cancer, and the effect is cumulative.
Sunscreen is essential to protect us against skin aging and cancer: True or False?
True, unequivocally, unless we live indoors and/or otherwise never go about under sunlight.
“But our ancestors—” lived under the same sun we do, and either used sunscreen or got advanced skin aging and cancer.
Sunscreen of times past ranged from mud to mineral lotions, but it’s pretty much always existed. Even non-human animals that have skin and don’t have fur or feathers, tend to take mud-baths in sunny parts of the world.
If you’d like to avoid oxybenzone and other chemicals, though, you might have your reasons. Maybe you’re allergic, or maybe you read that it’s a potential endocrine disruptor with estrogen-like and anti-androgenic properties that you don’t want.
There are other options, to include physical blockers containing zinc and titanium dioxide, which are generally recognized as safe and effective ingredients.
If you’re interested, you can even make your own sunscreen that blocks both UVA and UVB rays (UVA is what causes skin cancer; UVB is “milder” and is what causes sunburn):
Share This Post
Learn To Grow
Sign up for weekly gardening tips, product reviews and discounts.




