Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
From Apples to Bees, and high-fructose C’s: The truth about sugar and its impact on our health. Mythbusting and uncovering the facts.

From Apples to Bees, and high-fructose C’s
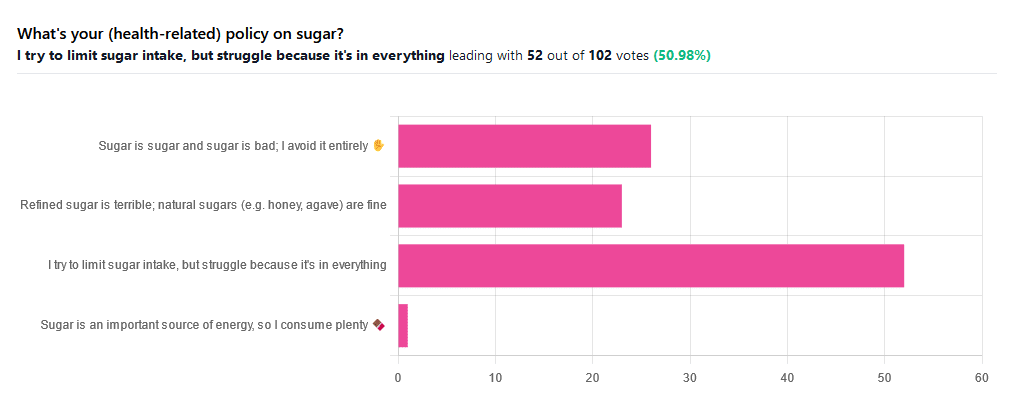
We asked you for your (health-related) policy on sugar. The trends were as follows:
- About half of all respondents voted for “I try to limit sugar intake, but struggle because it’s in everything”
- About a quarter of all respondents voted for “Refined sugar is terrible; natural sugars (e.g. honey, agave) are fine”
- About a quarter of all respondents voted for “Sugar is sugar and sugar is bad; I avoid it entirely”
- One (1) respondent voted for “Sugar is an important source of energy, so I consume plenty”
Writer’s note: I always forget to vote in these, but I’d have voted for “I try to limit sugar intake, but struggle because it’s in everything”.
Sometimes I would like to make my own [whatever] to not have the sugar, but it takes so much more time, and often money too.
So while I make most things from scratch (and typically spend about an hour cooking each day), sometimes store-bought is the regretfully practical timesaver/moneysaver (especially when it comes to condiments).
So, where does the science stand?
There has, of course, been a lot of research into the health impact of sugar.
Unfortunately, a lot of it has been funded by sugar companies, which has not helped. Conversely, there are also studies funded by other institutions with other agendas to push, and some of them will seek to make sugar out to be worse than it is.
So for today’s mythbusting overview, we’ve done our best to quality-control studies for not having financial conflicts of interest. And of course, the usual considerations of favoring high quality studies where possible Large sample sizes, good method, human subjects, that sort of thing.
Sugar is sugar and sugar is bad: True or False?
False and True, respectively.
- Sucrose is sucrose, and is generally bad.
- Fructose is fructose, and is worse.
Both ultimately get broken down into glycogen (if not used immediately for energy), but for fructose, this happens mostly* in the liver, which a) taxes it b) goes very unregulated by the pancreas, causing potentially dangerous blood sugar spikes.
This has several interesting effects:
- Because fructose doesn’t directly affect insulin levels, it doesn’t cause insulin insensitivity (yay)
- Because fructose doesn’t directly affect insulin levels, this leaves hyperglycemia untreated (oh dear)
- Because fructose is metabolized by the liver and converted to glycogen which is stored there, it’s one of the main contributors to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (at this point, we’re retracting our “yay”)
Read more: Fructose and sugar: a major mediator of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
*”Mostly” in the liver being about 80% in the liver. The remaining 20%ish is processed by the kidneys, where it contributes to kidney stones instead. So, still not fabulous.
Fructose is very bad, so we shouldn’t eat too much fruit: True or False?
False! Fruit is really not the bad guy here. Fruit is good for you!
Fruit does contain fructose yes, but not actually that much in the grand scheme of things, and moreover, fruit contains (unless you have done something unnatural to it) plenty of fiber, which mitigates the impact of the fructose.
- A medium-sized apple (one of the most sugary fruits there is) might contain around 11g of fructose
- A tablespoon of high-fructose corn syrup can have about 27g of fructose (plus about 3g glucose)
Read more about it: Effects of high-fructose (90%) corn syrup on plasma glucose, insulin, and C-peptide in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and normal subjects
However! The fiber content (in fruit) mitigates the impact of the fructose almost entirely anyway.
And if you take fruits that are high in sugar and/but high in polyphenols, like berries, they now have a considerable net positive impact on glycemic health:
- Polyphenols and Glycemic Control
- Polyphenols and their effects on diabetes management: A review
- Dietary polyphenols as antidiabetic agents: Advances and opportunities
You may be wondering: what was that about “unless you have done something unnatural to it”?
That’s mostly about juicing. Juicing removes much (or all) of the fiber, and if you do that, you’re basically back to shooting fructose into your veins:
- Effect of Fruit Juice on Glucose Control and Insulin Sensitivity in Adults: A Meta-Analysis of 12 Randomized Controlled Trials
- Intake of Fruit, Vegetables, and Fruit Juices and Risk of Diabetes in Women
Natural sugars like honey, agave, and maple syrup, are healthier than refined sugars: True or False?
True… Sometimes, and sometimes marginally.
This is partly because of the glycemic load. The glycemic index scores tail off thus:
- table sugar = 65
- maple syrup = 54
- honey = 46
- agave syrup = 15
So, that’s a big difference there between agave syrup and maple syrup, for example.
Note, incidentally, that table sugar, sucrose, is a disaccharide, and is 50% glucose and 50% fructose.
The other more marginal health benefits come from that fact that natural sugars are usually found in foods high in other nutrients. Maple syrup is very high in manganese, for example, and also a fair source of other minerals.
But… Because of its GI, you really don’t want to be relying on it for your nutrients.
Wait, why is sugar bad again?
We’ve been covering mostly the more “mythbusting” aspects of different forms of sugar, rather than the less controversial harms it does, but let’s give at least a cursory nod to the health risks of sugar overall:
- Obesity and associated metabolic risk
- Main contributor to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- Increased risk of heart disease
- Insulin resistance and diabetes risk
- Cellular aging (shortened telomeres)
- 95% increased cancer risk
That last one, by the way, was a huge systematic review of 37 large longitudinal cohort studies. Results varied depending on what, specifically, was being examined (e.g. total sugar, fructose content, sugary beverages, etc), and gave up to 200% increased cancer risk in some studies on sugary beverages, but 95% increased risk is a respectable example figure to cite here, pertaining to added sugars in foods.
And finally…
The 56 Most Common Names for Sugar (Some Are Tricky)
How many did you know?
Share This Post
Learn To Grow
Sign up for weekly gardening tips, product reviews and discounts.




