Could not getting enough sleep increase your risk of type 2 diabetes?
Sleep less than six hours? Your risk of type 2 diabetes could be higher. Study sheds light on the complex sleep-diabetes link.

Not getting enough sleep is a common affliction in the modern age. If you don’t always get as many hours of shut-eye as you’d like, perhaps you were concerned by news of a recent study that found people who sleep less than six hours a night are at higher risk of type 2 diabetes.
So what can we make of these findings? It turns out the relationship between sleep and diabetes is complex.
The study
Researchers analysed data from the UK Biobank, a large biomedical database which serves as a global resource for health and medical research. They looked at information from 247,867 adults, following their health outcomes for more than a decade.
The researchers wanted to understand the associations between sleep duration and type 2 diabetes, and whether a healthy diet reduced the effects of short sleep on diabetes risk.
As part of their involvement in the UK Biobank, participants had been asked roughly how much sleep they get in 24 hours. Seven to eight hours was the average and considered normal sleep. Short sleep duration was broken up into three categories: mild (six hours), moderate (five hours) and extreme (three to four hours). The researchers analysed sleep data alongside information about people’s diets.
Some 3.2% of participants were diagnosed with type 2 diabetes during the follow-up period. Although healthy eating habits were associated with a lower overall risk of diabetes, when people ate healthily but slept less than six hours a day, their risk of type 2 diabetes increased compared to people in the normal sleep category.
The researchers found sleep duration of five hours was linked with a 16% higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes, while the risk for people who slept three to four hours was 41% higher, compared to people who slept seven to eight hours.
One limitation is the study defined a healthy diet based on the number of servings of fruit, vegetables, red meat and fish a person consumed over a day or a week. In doing so, it didn’t consider how dietary patterns such as time-restricted eating or the Mediterranean diet may modify the risk of diabetes among those who slept less.
Also, information on participants’ sleep quantity and diet was only captured at recruitment and may have changed over the course of the study. The authors acknowledge these limitations.
Why might short sleep increase diabetes risk?
In people with type 2 diabetes, the body becomes resistant to the effects of a hormone called insulin, and slowly loses the capacity to produce enough of it in the pancreas. Insulin is important because it regulates glucose (sugar) in our blood that comes from the food we eat by helping move it to cells throughout the body.
We don’t know the precise reasons why people who sleep less may be at higher risk of type 2 diabetes. But previous research has shown sleep-deprived people often have increased inflammatory markers and free fatty acids in their blood, which impair insulin sensitivity, leading to insulin resistance. This means the body struggles to use insulin properly to regulate blood glucose levels, and therefore increases the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Further, people who don’t sleep enough, as well as people who sleep in irregular patterns (such as shift workers), experience disruptions to their body’s natural rhythm, known as the circadian rhythm.
This can interfere with the release of hormones like cortisol, glucagon and growth hormones. These hormones are released through the day to meet the body’s changing energy needs, and normally keep blood glucose levels nicely balanced. If they’re compromised, this may reduce the body’s ability to handle glucose as the day progresses.
These factors, and others, may contribute to the increased risk of type 2 diabetes seen among people sleeping less than six hours.
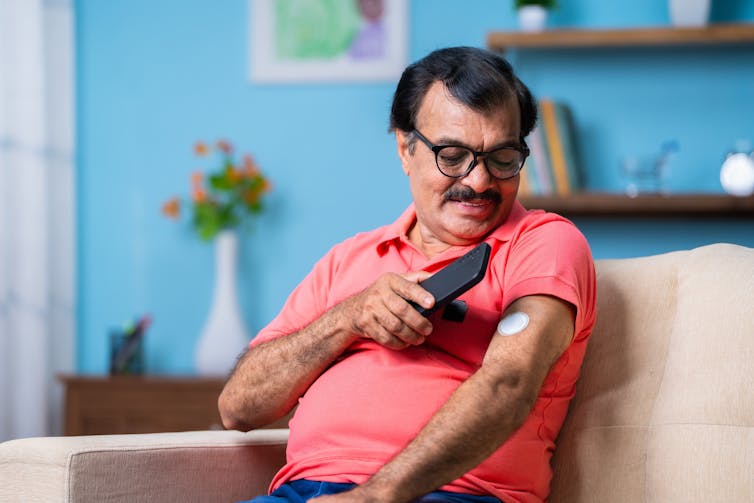

While this study primarily focused on people who sleep eight hours or less, it’s possible longer sleepers may also face an increased risk of type 2 diabetes.
Research has previously shown a U-shaped correlation between sleep duration and type 2 diabetes risk. A review of multiple studies found getting between seven to eight hours of sleep daily was associated with the lowest risk. When people got less than seven hours sleep, or more than eight hours, the risk began to increase.
The reason sleeping longer is associated with increased risk of type 2 diabetes may be linked to weight gain, which is also correlated with longer sleep. Likewise, people who don’t sleep enough are more likely to be overweight or obese.
Good sleep, healthy diet
Getting enough sleep is an important part of a healthy lifestyle and may reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Based on this study and other evidence, it seems that when it comes to diabetes risk, seven to eight hours of sleep may be the sweet spot. However, other factors could influence the relationship between sleep duration and diabetes risk, such as individual differences in sleep quality and lifestyle.
While this study’s findings question whether a healthy diet can mitigate the effects of a lack of sleep on diabetes risk, a wide range of evidence points to the benefits of healthy eating for overall health.
The authors of the study acknowledge it’s not always possible to get enough sleep, and suggest doing high-intensity interval exercise during the day may offset some of the potential effects of short sleep on diabetes risk.
In fact, exercise at any intensity can improve blood glucose levels.
Giuliana Murfet, Casual Academic, Faculty of Health, University of Technology Sydney and ShanShan Lin, Senior Lecturer, School of Public Health, University of Technology Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Learn To Grow
Sign up for weekly gardening tips, product reviews and discounts.